International Activities In The Field Of Food Additives
Inspiring product
EXOVIO offers a comprehensive range of Foam Control Agents (FCA) to the food processing industry
Antifoams or foam inhibitors are usually added to the foaming solution prior to foam formation and act to prevent formation of excessive foam. In contrast, Defoamers or foam breakers are substances sprinkled over existing foam with major aim to induce rapid foam collapse. The activity of antifoam is strongly depending on entry barrier, which indicates how difficult is for predispored antifoam entities to pierce the gas-water interface and to appear on the solution surface. However, in the case of Defoamers the entry barriers are less important because the Defoamers are introduced from the gas phase and there is no barrier to prevent the emergence on the gas-water interface.
A typical antifoam or defoamer consists of oil, hydrophobic solid particles or a mixture of both. Nonpolar oils (mineral oils, silicone oils) and polar oils (fatty alcohols and acids, alkyl amines, alkyl amides, tributhyl phosphate (TBP), tioethers and many others) have been successfully used. The solid particle could be inorganic (silica, Al2O3, TiO2), wax (e.g. Mg stearate) or polymeric (e.g. poly amides, poly propylene).
Foam Control Agents (Defoaming, Antifoam and Air release)
A defoamer or an anti-foaming agent is a chemical additive that reduces and hinders the formation of foam in process liquids. The terms anti-foam agent and defoamer are often used interchangeably. Commonly used agents are insoluble oils, polydimethylsiloxanes and other silicones, certain alcohols, stearates and glycols. The additive is used to prevent formation of foam or is added to break a foam already formed.
In industrial processes, foams pose serious problems. They cause defects on surface coatings and prevent the efficient filling of containers. A variety of chemical formulae are available to prevent formation of foams.
For this reason, the chemical method is an attractive and cost effective choice to battle foam.
Causes side effect
The causes of foaming are many. The most common include:
| · Water contamination | · Solids contamination |
| · Mechanical issues (causing excessive aeration of the fluid) | · Contamination of the fluid with grease |
| · Cross contamination of the fluid with the wrong lubricant | |
| · Depleted defoaming (due to the use of excessively fine filtration and electrostatic separation technologies) | |
| · Overfilling of the sump with splash- and bath-lubricated compartments | |
| · Too much defoaming additive, either by incorrect formulation or by incorrect reconstruction (sweetening) of the additive package | |
Defoaming Mechanism
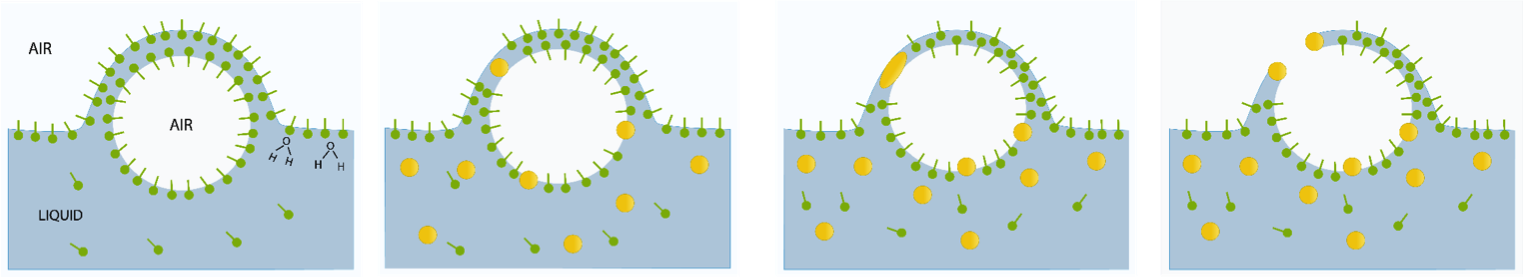
- Defoamer is Surface Active agent that destroys foam after it has formed.
- an antifoam agent is an additive that prevents foaming.
- The key to defoaming is to disrupt the surfactant stabilized foam lamella.
Types of Food Control Agents – FCA’s-:
The industry supplies a wide range of different foam control agents. The most widely known classes of FCA’s are:
- Silicones
Foam control agents for the food industry requires FDA approved grades, for this reason, not every type of FCA can be applied.
FOMA Foam™ Food grade:
| Applications | Type | Product |
| Sugar | Washing | FOMA Foam® PB 215 |
| FOMA Foam® PB 2236 | ||
| FOMA Foam® PD 25 | ||
| FOMA Foam® PO 1176 | ||
| Extraction | FOMA Foam® PD 67 | |
| FOMA Foam® PB 946 | ||
| FOMA Foam® PB 1892 | ||
| FOMA Foam® PO 2058 | ||
| FOMA Foam® PO 1078 | ||
| Antiscaling Agent | FOMA Foam® PBD 1720 | |
| FOMA Foam® PBL 4263 | ||
| Wetting Agent | FOMA Foam® PB 4214 | |
| Flocculating Agent | FOMA Foam® PBL 1611 | |
| Applications | Type | Product |
| Potatoes | French Fries/Chips | FOMA Foam® PB 7955 |
| FOMA Foam® PD 24 | ||
| FOMA Foam® PD 26 | ||
| Fermentation | Alcohol/ Yeast | FOMA Foam® PD 23 |
| FOMA Foam® PD 65 | ||
| FOMA Foam® PO 2989 | ||
| FOMA Foam® PB 5590 | ||
| FOMA Foam® PB 6880 | ||
| FOMA Foam® PBS 43 | ||
| FOMA Foam® PBF 43 | ||
| FOMA Foam® PBK 43 | ||
| Vegetable | FOMA Foam® PD 17 |
Temperatures have a strong influence on the FCA activity. Some FOMA Foam® grades are highly effective at specific temperature.
Notes:
- FCA’s used in the food processing industry are processing aids and do not remain in the food unless stated otherwise.
